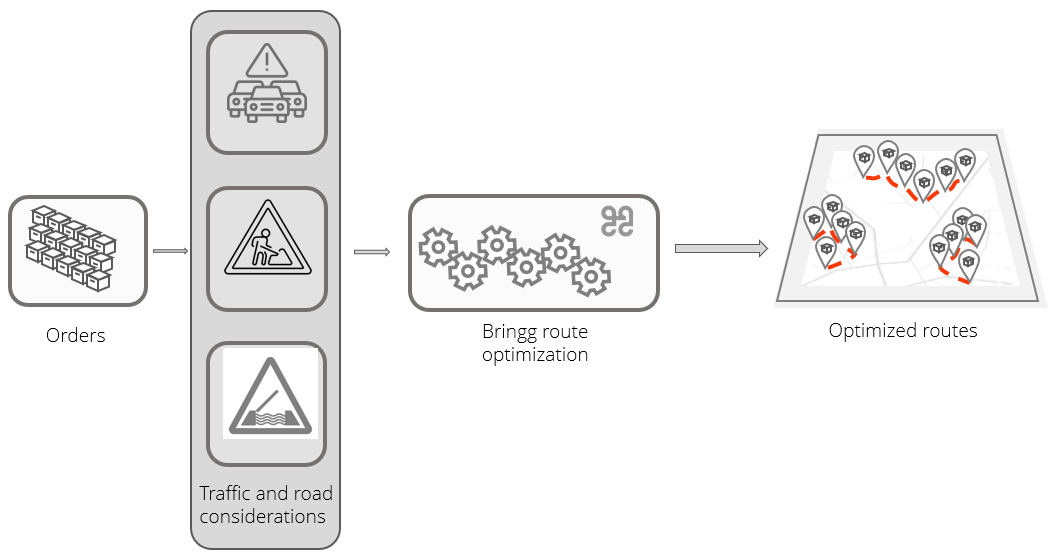
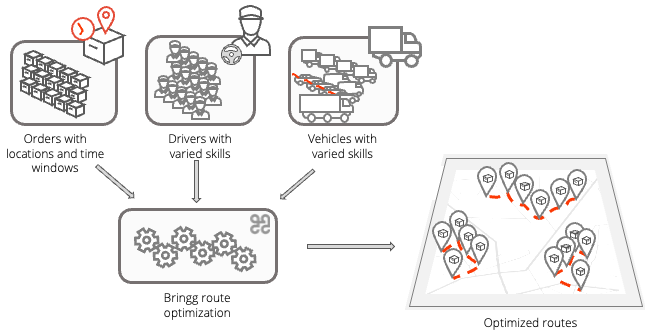
Run Bringg's route optimization (RO) to reduce costs by organizing your into the fastest, most efficient planned routes , where each order arrives at its destination within its designated time window. If you have an Own Fleet, RO can also assign each route to a vehicle or driver who is available at that time and has the correct skills to fulfill the orders. You can configure RO with preferences like the maximum length of a route, the time on site (TOS), the time to load the vehicle, predicted and real time traffic patterns, and so on.
For example, you can set route optimization (RO) to limit the number of destinations on a route, or to use the minimum number of vehicles in a route.
You can also:
- Add vehicle profiles to send more precise vehicle size and capacity restrictions to the optimization engine to create more accurate routes. Learn more.
 Set up Bringg's route optimization to create efficient routes
Set up Bringg's route optimization to create efficient routes Each time you run route optimization on the same group of orders you may well receive a different result, as there are multiple ways to organize the same group of orders into efficient routes. Instead of reshuffling all orders each time, you can set your optimizations to build on your existing plans. You can also make focused changes where they are required using the route planner.
Before You Begin
- Write down your detailed requirements of how you expect your drivers and vehicles to behave during their work shifts. Do vehicles they have a set starting location? Do you want longer or shorter routes? Do you want more smaller vehicles or fewer larger vehicles?
- Define the shifts and allocation of resources, by creating delivery blocks. Learn more.
Settings for Route Optimization
You can tailor the route optimization outputs to fit your needs, by configuring any of the following settings. You can configure certain settings yourself, and contact your Bringg customer service representative to implement others on your behalf.
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Start route at End route at | Specify the starting point and/or the final destinationof any route for this team or delivery block as:
Tip Resource-based optimization (type 6) allows you to set a default start and end location from a menu of options. Legacy optimization types allow you to choose simply whether to set the team location, often the fulfillment center, as the default. |
Start next route where previous route ended | Add a further starting point of a route as the end of the previous one. |
Minimize resources | Lower your costs by creating fewer routes using fewer resources (vehicles and drivers). One such method might be to prioritize using larger capacity vehicles. |
Predicted and real time traffic patterns | You can opt to add advanced traffic integration settings to RO to improve the efficiency and accuracy of your routes, as well as the estimated arrival times (ETA), and the selection of drivers. Advanced traffic integration considers past, historical, and predicted data during the optimization process to come up with the best possible routes for specific dates and times. It also considers road hazards and restrictions that are known in advance of the optimization. Then, once the order assignments are locked into place, traffic integration uses real time traffic and information about new hazards like collisions or road work to update the ETA. This ensures better oversight of routes from the control tower, and a more seamless consumer experience. Contact your Bringg customer service representative to add this to your configuration. Without this feature, RO predicts traffic based only on previous patterns:
During a route, drivers use their preferred mobile navigation app to see live traffic updates and avoid slow moving areas. You can even add a dedicated navigation app for the safe driving of heavy goods vehicles (HGV) (using Trimble's CoPilot, purchased separately, Android only). |
Allow the driver to reload | (Self-service) Ensure drivers can return to the fulfillment center between routes, and allow time for breaks and loading vehicles for the next route. You can also configure RO to automatically estimate the loading or unloading times at the start or end of routes based on the amount of goods and the types of goods for that route. |
Service area | If you assign drivers to specific , you can limit routes using those drivers to destinations in that area. A team can have more than one service area. |
Allow route tweaks | Select to allow you to tweak a route to add unassigned orders. |
Driver admin time | You can configure RO to add to the ETOS of a destination when you need to perform a specific driver action. |
Maximum total distance per route | Configure the maximum distance of a single route. As you lengthen routes, RO can create fewer to cover the same number of orders. |
Maximum total time per route | Define the longest time a single driver can work on a single route. As you lengthen routes, RO can create fewer to complete the same number of orders. |
Maximum destinations per route | Define the maximum number of destinations on a single route. More destinations means fewer routes to complete the same number of orders. |
Maximum capacity | (Self-service) In the vehicle profile settings, define the maximum load in a single vehicle/trailer for a single route. |
Define on-time orders | You can allow RO to schedule arrivals at destinations so that:
|
Driver fairness | Use the Driver Fairness setting to encourage more evenly distributed workloads for each driver in a shift, supporting a more fair and equal approach with your delivery workforce. |
| Use all drivers | If enabled, the optimization will prioritize assigning orders to all the drivers who are on shift and available instead of creating fewer routes with fewer drivers. |
Route clustering | (Self-service) Use Route Clustering to create routes with far fewer intersections. Optimized routes sometimes crisscross each other, taking some drivers through the same streets or areas. 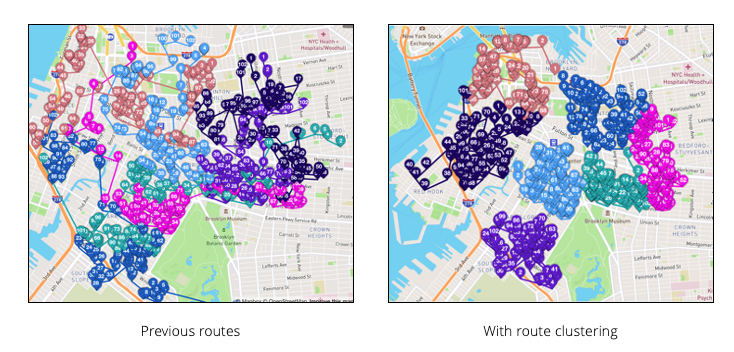 Reduce intersecting routes with clustering Reduce intersecting routes with clustering
|
Avoid non-commercial roads | Configure RO to avoid roads which do not allow commercial vehicles (supported in the US only). Note Not compatible with Vroom. |
| Avoid toll roads | Indicate whether or not you want RO to use toll roads in planning routes. Note This setting is required in the United States. |
Display routes on roads in route planner | (Default behavior) Configure the route planner to display the actual directions of the optimized routes which connect the destinations. |
Keep previous route unless explicitly overwrite | (Enabled by default) Configure RO to keep the existing route definitions unless you explicitly want to re-optimize the orders. |
Create routes in the future | (Enabled by default) Assume RO needs to create routes where all destinations are after this moment in time. |
| Willingness to wait | Indicate to RO to what extent it is an issue for a driver to wait between orders. |
| Reshuffle or preserve sequence when adding orders to already optimized routes | Configure RO to either change the priority of any of the orders now in the route, or maintain the same order of priorities while inserting new orders where they slot into those priorities. |
| Squash time | Indicate how much time RO should add for every order after the first one, which is delivered to the same address and customer as the first. |
| Max route radius | Configure RO to set an aerial distance limit of any route from the driver start location. |
Required Inputs for Route Optimization
The which you optimize into routes should contain the following details:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Time window | A time window is the time range when you intend to fulfill an order. Therefore, an order is considered fulfilled on time if it arrives within the time window. The time window is set when you schedule an order in Bringg and is usually defined by the no_earlier_than and no_later_than fields. Narrower time windows are seen as better service, like 9 to 10 am, while longer windows are more typical of larger carriers. |
Estimated Time on Site (ETOS) | Time on site starts when a driver arrives () at a destination on a route, and ends when they leave () to continue to the next destination. This can include finding parking, gaining access to the building, security passes, elevators, onsite activities like payment, assembly, unpacking and so on, then exiting, and returning to the vehicle ready to leave. Bringg uses the time between check-in and checkout to (ETA) at the following destinations in a route. You can choose between:
|
Type of order | The type of order can have an impact on its ETOS. An order can be:
|
Service plan | A service plan is a type of service that you provide to consumers like express, basic, or over the threshold. Service plans enable you to fulfill service level agreements by letting the Bringg Platform, dispatchers, and drivers know when you have committed to providing a specific service, such as delivery at the customer's home or workplace, or a specific handoff procedure like requiring the customer's signature as proof of delivery. |
Order's skills | Set up skills in Bringg to automatically assign orders to routes with the right drivers and vehicles that have the capabilities necessary to fulfill them. For example, when delivering groceries you can set up a |
Ranking | Some orders can have a rank signifying how important they are. High ranked orders must be delivered as a matter of priority, while a lower ranked order may be moved to the next route. |
Weight | The weight of the goods in lbs or kg. |
Dimensions | The dimensions of the goods in terms of their height, width, length and volume. Tip Bringg can send the output of a route to a specialist loader applications which position and sequence the goods loaded in the vehicle. |
Fragile | If an order's goods are fragile, they must be on top. This is applicable for use with specialist loader apps. |
Palette | Sometimes an item must be on the bottom of an order's goods, like a palette, for use with specialist loader apps. |
Routes, Drivers or vehicles should also have the following details:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Maximum vehicle capacity | Derived from the vehicle type, measured in ft/m, or as weight in lbs/kg. |
Cost per km or mile | (Legacy RO only) Define the cost of using this driver and/or vehicle, to help pick the most cost effective combination of drivers, vehicles and routes. Define the cost when driving and when waiting, stored in the vehicle type. |
Availability | RO checks the delivery blocks, and factors in break times, and vehicle loading times (see Driver admin time). |
Limited to service area | Limit this driver or vehicle to destinations in a specific service area. |
Default start location | Defines the default location of the vehicle at the start of a route. |
Default end location | Defines the default location of the vehicle at the end of a route. |
Skills (Driver or Vehicle) | Set up skills in Bringg to automatically assign orders to routes with the right drivers and vehicles that have the capabilities necessary to fulfill them. For example, when delivering groceries you can set up a |