Once you connect with a selected Carrier via the carrier catalog, update your API and CSV payloads to include the fields that the carrier requires. Then you can test your communication with their sandbox and production accounts before going live.
You can also check the required fields before connecting with the carrier.
Before You Begin
- Confirm you have a Bringg user of type Admin.
- Connect with your preferred carrier using the catalog.
Ensure you have their credentials to communicate with both their sandbox and production accounts. Learn more. - Coordinate with your IT integrator to ensure successful integration.
Procedure
Step 1: Verify that your payloads meet the carrier's requirements.
With your IT integrator, send an API or CSV payload with a test order.
If you have already begun sending payloads to Bringg, you can skip this step. Learn more.
If you are connecting with DriveYello, Doordash, Uber, Zenkraft, Roadie, or Lyft, continue to step 2. For all other carriers, skip to step 4.
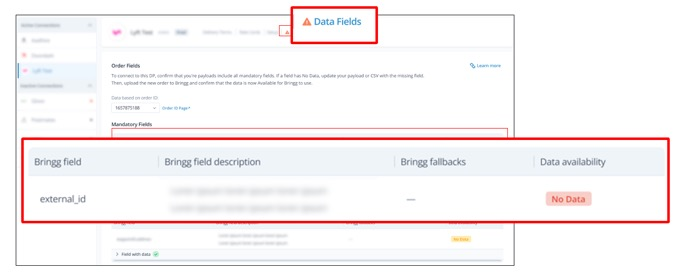
Step 2: Compare your payload with the carrier-required fields, which have already been mapped to Bringg's API fields.
Go to Delivery Hub > My Delivery Providers, select the carrier and choose the Data Fields tab to see the list of required and optional fields.
 Open a carrier's list of fields
Open a carrier's list of fields
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Bringg field | The name of the API field where Bringg looks for the data that the Bringg requires. |
Bringg field description | This description describes what is included in the field. |
Bringg fallbacks | If the field listed under Bringg field is empty or missing, the carrier will look in the fallback field to find the required data. |
Data availability | This field tells you if Bringg found data in the required field. |
Step 3: With your IT integrator, add any missing data fields to your payloads and send a new test order to Bringg.
Step 4: Continue your integration by sending test payloads to the carrier's sandbox account, then to their production account.
Step 5: Once you have integrated with a new carrier, implement them in your order flow:
- Add to define the abilities of each Bringg so that Bringg can assign Bringgs that supports the requirements of each order. Learn more.
- Set up rate cards with the financial terms that you have contracted with your carrier so that Bringg can calculate cheapest carrier for each order and provide a cost estimate before you receive your invoice from the carrier. Learn more.
- Set up Bringg's carrier selector to automatically assign the best carrier for each order, in line with your business priorities and delivery strategy.